Channel Biology and Electrophysiology Research
Each of our hearts contains several billion individual muscle cells. Every second of our lives, these billions of cells need to contract and relax together for the heart to work effectively as a pump. Fortunately, our hearts have an electrical system that coordinates the individual cells, telling them when to contract and when to relax—the electrical system functions of bioelectricity. The cells have individual ion channels that allow bioelectrical current in the form of charged ions to flow across the cell membrane, changing the voltage across each membrane. The cells also have channels between them, allowing the rapid spread of bioelectrical ions across the heart. A disturbance of the heart’s electrical system is caused by an arrhythmia. Severe arrhythmias can cause the heart to stop, which is responsible for up to 300,000 deaths per year in the United States. At the CVRTI, we have a long history of pioneering in the field of electrophysiology research, including the genetic and acquired basis of heart electricity and heart arrhythmias. Investigators are now developing innovative methods to treat heart arrhythmias and prevent their occurrence, aiming to safeguard heart health through the understanding of channels, biology, and membrane proteins involved in cardiac bioelectricity.
Publications
Auxiliary Trafficking Subunit GJA1-20k Protects Connexin43 from Degradation and Limits Ventricular Arrhythmias.
This study introduces how a protein formed by internal translation of Connexin43 mRNA is essential for the gap junction based electrical communication of each heartbeat. Without it, arrhythmias and sudden death occur. The study introduces how cardiac ion channels can generate their own trafficking subunits. https://www.jci.org/articles/view/134682
Xiao S, Shimura D, Baum R, Hernandez DM, Agvanian S, Nagaoka Y, Katsumata M, Lampe PD, Kleber AG, Hong T, Shaw RM. Auxiliary Trafficking Subunit GJA1-20k Protects Connexin43 from Degradation and Limits Ventricular Arrhythmias. JCI, 2020; 130(9):4858-4870.
Cardiac BIN1 Folds T-tubule Membrane, Controlling Ion Flux and Limiting Arrhythmia.
This study introduces a new concept how heart muscle is organized and identifies a new cardiac protein (cardiac BIN1 or cBIN1) which is responsible for the microarchitecture of heart muscle cells allowing channels such as the L-type calcium channel to localize to its correct subdomain. https://www.nature.com/articles/nm.3543
Hong T, Yang H, Zhang S, Cho HC, Kalashnikova M, Sun B, Zhang H, Bhargava A, Grabe M, Olgin J, Gorelik J, Marbán E, Jan LY, Shaw RM. Cardiac BIN1 folds T-tubule membrane, controlling ion flux and limiting arrhythmia. Nature Medicine, 2014; 20:624-32.
Direct Comparison of a Novel Antitachycardia Pacing Algorithm Against Present Methods Using Virtual Patient Modeling.
Anti-tachycardia pacing is routinely used to terminate ventricular arrhythmias but its success can be limited. In this joint project with Medtronic and the Scientific Computing Institute at University of Utah, the team tested a new adaptive algorithm for ATP in computational models based on patient specific scar and arrhythmia data showing a higher success rate.https://www.heartrhythmjournal.com/article/S1547-5271(20)30430-6/fulltext
Swenson DJ, Taepke RT, Blauer JJE, Kwan E, Ghafoori E, Plank G, Vigmond E, MacLeod RS, DeGroot P, Ranjan R. Direct comparison of a novel antitachycardia pacing algorithm against present methods using virtual patient modeling. Heart Rhythm, 2020; 17(9):1602-1608.
Electrophysiological Modeling of Fibroblasts and Their Interaction with Myocytes.
In this study, we developed a mathematical model of fibroblast electrophysiology based on data from whole-cell patch clamp and polymerase chain reaction studies. We studied electrical bridging between ventricular myocytes via fibroblast insets for various coupling resistors. The simulations support the hypothesis that coupling of fibroblasts to myocytes modulates electrophysiology of cardiac cells and tissues.https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007%2Fs10439-007-9405-8
Sachse FB, Moreno AP, Abildskov JA. Electrophysiological modeling of fibroblasts and their interaction with myocytes. Ann Biomed Eng, 2008; 36(1):41-56.
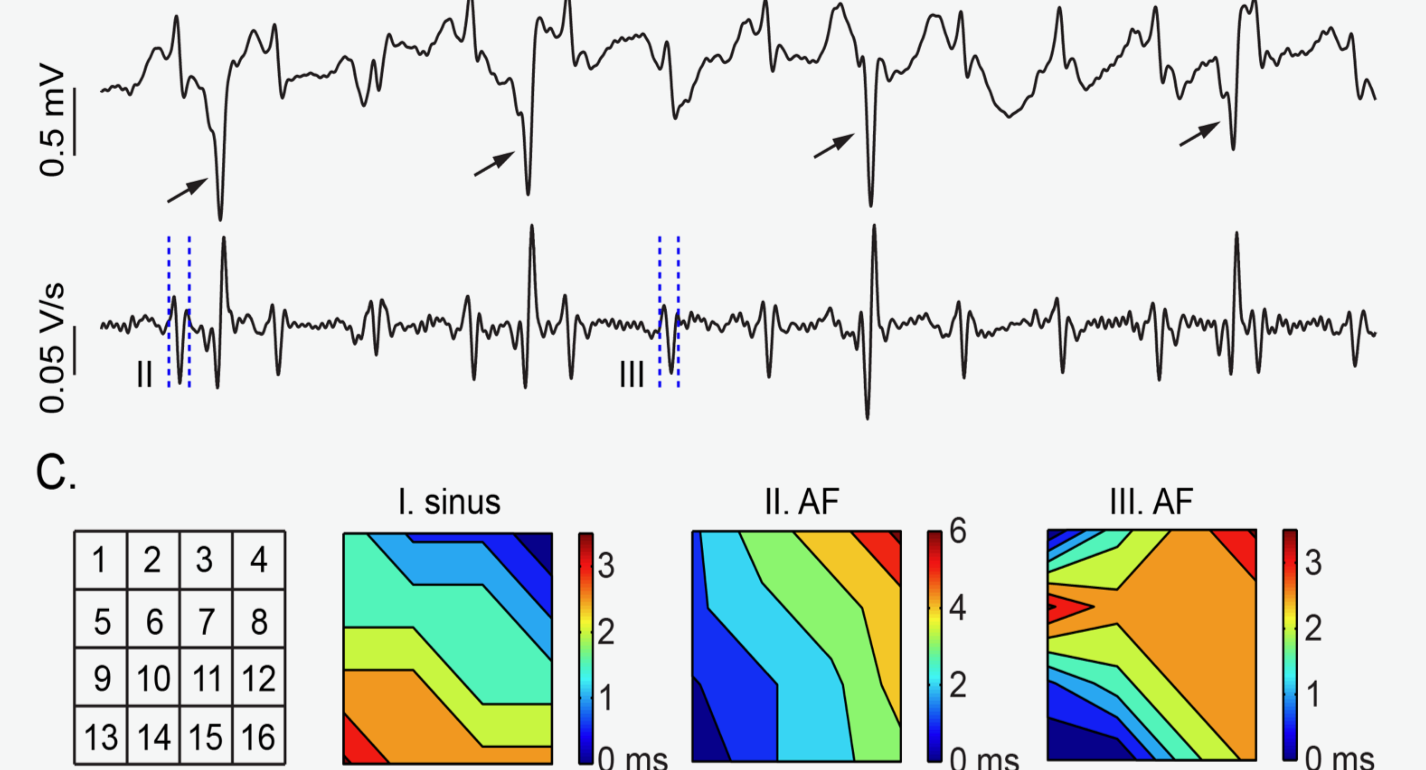
Endocardial Activation Drives Activation Patterns During Long-Duration Ventricular Fibrillation and Defibrillation.
In this study, transmural and endocardial cardiac mapping techniques were used to demonstrate that the endocardium and Purkinje fiber system plays a critical role in driving the rapid activation rate during ventricular fibrillation. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/full/10.1161/CIRCEP.117.005562
Panitchob N, Li L, Huang J, Ranjan R, Ideker RE, Dosdall DJ. Endocardial Activation Drives Activation Patterns During Long-Duration Ventricular Fibrillation and Defibrillation. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol, 2017; 10(12).
GJA1-20k Arranges Actin to Guide Cx43 Delivery to Cardiac Intercalated Discs.
This study introduces how the actin cytoskeleton works with subunits of an ion channel (Connexin43) to arrange trafficking pathways for delivery of the full length channel. This pathway is disrupted in cardiac disease such as cardiac ischemia. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.117.311955
Basheer WA, Xiao S, Epifantseva I, Fu Y, Kleber AG, Hong TT, Shaw RM. GJA1-20k arranges actin to guide Cx43 delivery to cardiac intercalated discs. Circ Res, 2017; 121:1069-1080.
His Bundle Pacing Shows Similar Ventricular Electrical Activation as Sinus; Selective and Non-Selective His Pacing Indistinguishable.
Traditional pacing locations with a single lead in the right ventricle may lead to ventricular dyssynchrony and the development of heart failure. In this study, 256 epicardial and endocardial electrodes were used to compare the activation sequence of pacing in the right ventricle, biventricular pacing, and selective and non-selective His bundle pacing. The activation sequence of both selective and non-selective His bundle pacing was indistinguishable from normal sinus rhythm, while biventricular and RV pacing had slower and more dyssynchronous ventricular activation sequences. Mechanical dysfunction is less likely to develop from His bundle pacing as compared to other clinically relevant pacing locations. https://journals.physiology.org/doi/abs/10.1152/ajpheart.00292.2020?af=R&
Hirahara AM, Lange M, Shah A, Khan MS, Ranjan R, Stoddard G, Dosdall DJ.His Bundle Pacing Shows Similar Ventricular Electrical Activation as Sinus; Selective and Non-Selective His Pacing Indistinguishable. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol, 2020; doi:10.1152/ajpheart.00292.2020.
In Mice Subjected to Chronic Stress, Exogenous cBIN1 Preserves Calcium-Handling Machinery and Cardiac Function.
This study introduces the role of cBIN1-microdomains in organizing intracellular distribution of SERCA2a for efficient diastolic calcium removal. Thus, through regulating systolic calcium release at dyads and diastolic calcium removal via SERCA2a, cBIN1-microdomains are critical in cardiac inotropy and lusitropy.https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2452302X20301212?via%3Dihub
Liu Y, Zhou K, Li J, Agvanian S, Caldaruse AM, Shaw S, Hitzeman TC, Shaw RM, Hong T. In Mice Subjected to Chronic Stress, Exogenous cBIN1 Preserves Calcium-Handling Machinery and Cardiac Function. JACC Basic Transl Sci, 2020; 5(6), 561-578.
Isoproterenol Promotes Rapid Ryanodine Receptor Movement to Bridging Integrator 1 (BIN1)-Organized Dyads.
This study introduces the mechanisms of dynamic regulation of dyad microdomains during an acute stress response. Cardiomyocyte cBIN1 microdomains are found to be responsive to acute beta-adrenergic activation for subsequent organization between L-type calcium channels and ryanodine receptors for efficient excitation-contraction coupling. https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/epub/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.115.018535
Fu Y, Shaw SA, Naami R, Vuong CL, Basheer WA, Guo X, Hong T. Isoproterenol Promotes Rapid Ryanodine Receptor Movement to Bridging Integrator 1 (BIN1)-Organized Dyads. Circulation, 2016; 133(4), 388-97.
Location and Function of Transient Receptor Potential Canonical Channel 1 in Ventricular Myocytes.
This study provides evidence for a role of transient receptor canonical channels 1 (TRPC1) as a contributor to sarcoplasmic calcium leak in cardiomyocytes, which was previously explained by ryanodine receptors only. We propose that the findings will guide us to an understanding of TRPC1 channels as modulators of cytosolic and contractility in cardiomyocytes. https://www.jmmc-online.com/article/S0022-2828(20)30020-1/fulltext
Hu Q, Ahmad AA, Seidel T, Hunter C, Streiff M, Nikolova L, Spitzer KW, Sachse FB. Location and function of transient receptor potential canonical channel 1 in ventricular myocytes. J Mol Cell Cardiol, 2020; 139:113-123.
Real-Time Magnetic Resonance Imaging-Guided Cryoablation of the Pulmonary Veins with Acute Freeze-Zone and Chronic Lesion Assessment.
Current ablation techniques are not geared towards seeing real time changes to tissue as it is ablated. Real time MRI can provide that capability. In this study, the team looked at changes to tissue and the catheter using real time MRI when doing cryo ablation. It shows the growth of the freeze zone in real time but changes to tissue as well while using the cryo balloon. https://academic.oup.com/europace/article/21/1/154/5033540
Lichter J, Kholmovski EG, Coulombe N, Ghafoori E, Kamali R, MacLeod R, Ranjan R. Real-time magnetic resonance imaging-guided cryoablation of the pulmonary veins with acute freeze-zone and chronic lesion assessment. Europace. 2019; 21(1):154-162.
Reproducibility of Clinical Late Gadolinium Enhancement Magnetic Resonance Imaging in Detecting Left Atrial Scar After Atrial Fibrillation Ablation.
MRI has been used to see atrial scar but with limited data on reliability and reproducibility. In this study, the Ranjan laboratory systematically evaluated post ablation atrial scar reproducibility in clinical atrial MRI scans and showed that ablation related high intensity areas are very reproducible in clinical scans. https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/abs/10.1111/jce.14743
Kamali R, Schroeder J, DiBella E, Steinberg B, Han F, Dosdall DJ, Macleod RS, Ranjan R. Reproducibility of clinical late gadolinium enhancement magnetic resonance imaging in detecting left atrial scar after atrial fibrillation ablation. J Cardiovasc Electrophysiol, 2020; doi: 10.1111/jce.14743.
Restitution Characteristics of His Bundle and Working Myocardium in Isolated Rabbit Hearts.
In this study, we used microelectrode impalements of the His bundle and the working myocardium to investigate the restitution characteristics of the His bundle at different activation rates. We demonstrated that the His bundle action potential duration was shorter than that of the working myocardium at both slow and rapid activation rates. This may permit the His bundle to be an active part of reentrant activity in fast arrhythmias such as ventricular tachycardia and fibrillation. https://dx.plos.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0186880
Huang S, Wu L, Huang J, Panitchob N, Hu N, Ranjan R, Dosdall DJ. Restitution characteristics of His bundle and working myocardium in isolated rabbit hearts. PLoS One, 2017; 12(10):e0186880.
Sheet-Like Remodeling of the Transverse Tubular System in Human Heart Failure Impairs Excitation-Contraction Coupling and Functional recovery by Mechanical Unloading.
This study showed a new type of sheet-like t-system remodeling of human failing cardiomyocytes characterized by large distances between sacrolemmal L-type calcium channels and clusters of junctional ryanodine receptors in the sarcoplasmic reticulum. This resulted in asynchronous calcium release and ineffective excitation-contraction coupling which precluded functional myocardial recovery of failing hearts.https://www.ahajournals.org/doi/abs/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.116.024470
Seidel T, Navankasattusas S, Ahmad A, Diakos NA, Xu WD, Tristani-Firouzi M, Bonios MJ, Taleb I, Li DY, Selzman CH, Drakos SG*, Sachse FB*. Sheet-like remodeling of the transverse tubular system in human heart failure impairs excitation-contraction coupling and functional recovery by mechanical unloading. Circulation, 2017; 25;135(17):1632 45.
Structural basis of Action for a Human Ether-a-go-go-Related Gene 1 Potassium Channel Activator.
Activation of human ether-a-go-go-related gene 1 (hERG1) potassium channels mediates cardiac action potential repolarization. These findings define a putative binding site for the activator RPR and confirm the importance of an interaction between the S4–S5 linker and the S6 domain in electromechanical coupling of voltage-gated potassium channels.https://www.pnas.org/content/104/34/13827.short
Perry M, Sachse FB, Sanguinetti, MC. Structural basis of action for a human ether-a-go-go-related gene 1 potassium channel activator. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2007; 104(34), 13827-13832.

 The Dosdall Laboratory, headed by Derek Dosdall, PhD, focuses on using whole heart mapping and microelectrode techniques to investigate the role of the ventricular conduction system on arrhythmia onset and maintenance. Link to lab summary page on CVRTI
The Dosdall Laboratory, headed by Derek Dosdall, PhD, focuses on using whole heart mapping and microelectrode techniques to investigate the role of the ventricular conduction system on arrhythmia onset and maintenance. Link to lab summary page on CVRTI  The Drakos Laboratory, headed by Stavros Drakos, MD, PhD, through an ongoing collaboration with the Sachse Laboratory, studies how cardiac ion channels are distributed and how channels clustered to specific subdomains of cardiac cell membrane affect excitation-contraction coupling in healthy, failing, and recovering heart muscle. Link to lab summary page on CVRTI
The Drakos Laboratory, headed by Stavros Drakos, MD, PhD, through an ongoing collaboration with the Sachse Laboratory, studies how cardiac ion channels are distributed and how channels clustered to specific subdomains of cardiac cell membrane affect excitation-contraction coupling in healthy, failing, and recovering heart muscle. Link to lab summary page on CVRTI 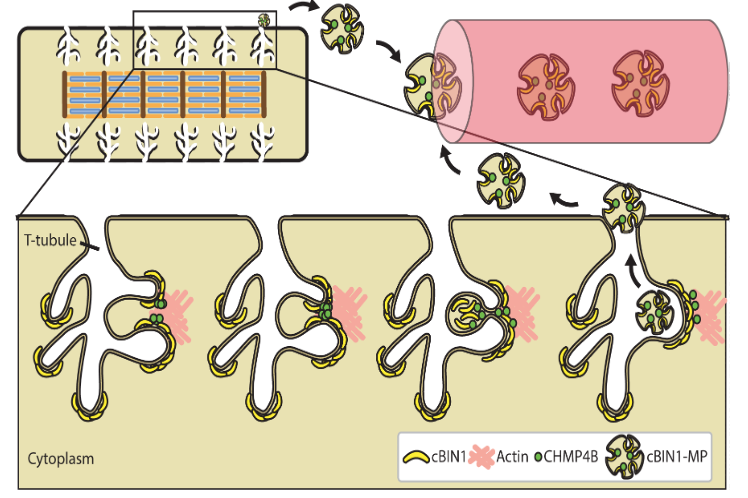 The Hong Laboratory, headed by TingTing Hong, MD, PhD, studies the regulation and remodeling of membrane microdomains of cardiomyocytes during heart failure progression. They study how cardiomyocyte surface microdomains are organized to concentrate ion channels and signaling proteins for proper function and regulation in normal and failing hearts. The research includes the mechanisms of scaffolding protein and cytoskeleton-based maintenance of membrane structures and subdomains important in calcium signaling, turnover mechanisms of microdomains, and the mechanisms of heart failure progression. The Hong lab’s goal is to identify, at the bench, new molecular and cellular targets that can be translated to develop new therapeutic tools for clinical management of heart failure.Link to lab summary page on CVRTI
The Hong Laboratory, headed by TingTing Hong, MD, PhD, studies the regulation and remodeling of membrane microdomains of cardiomyocytes during heart failure progression. They study how cardiomyocyte surface microdomains are organized to concentrate ion channels and signaling proteins for proper function and regulation in normal and failing hearts. The research includes the mechanisms of scaffolding protein and cytoskeleton-based maintenance of membrane structures and subdomains important in calcium signaling, turnover mechanisms of microdomains, and the mechanisms of heart failure progression. The Hong lab’s goal is to identify, at the bench, new molecular and cellular targets that can be translated to develop new therapeutic tools for clinical management of heart failure.Link to lab summary page on CVRTI 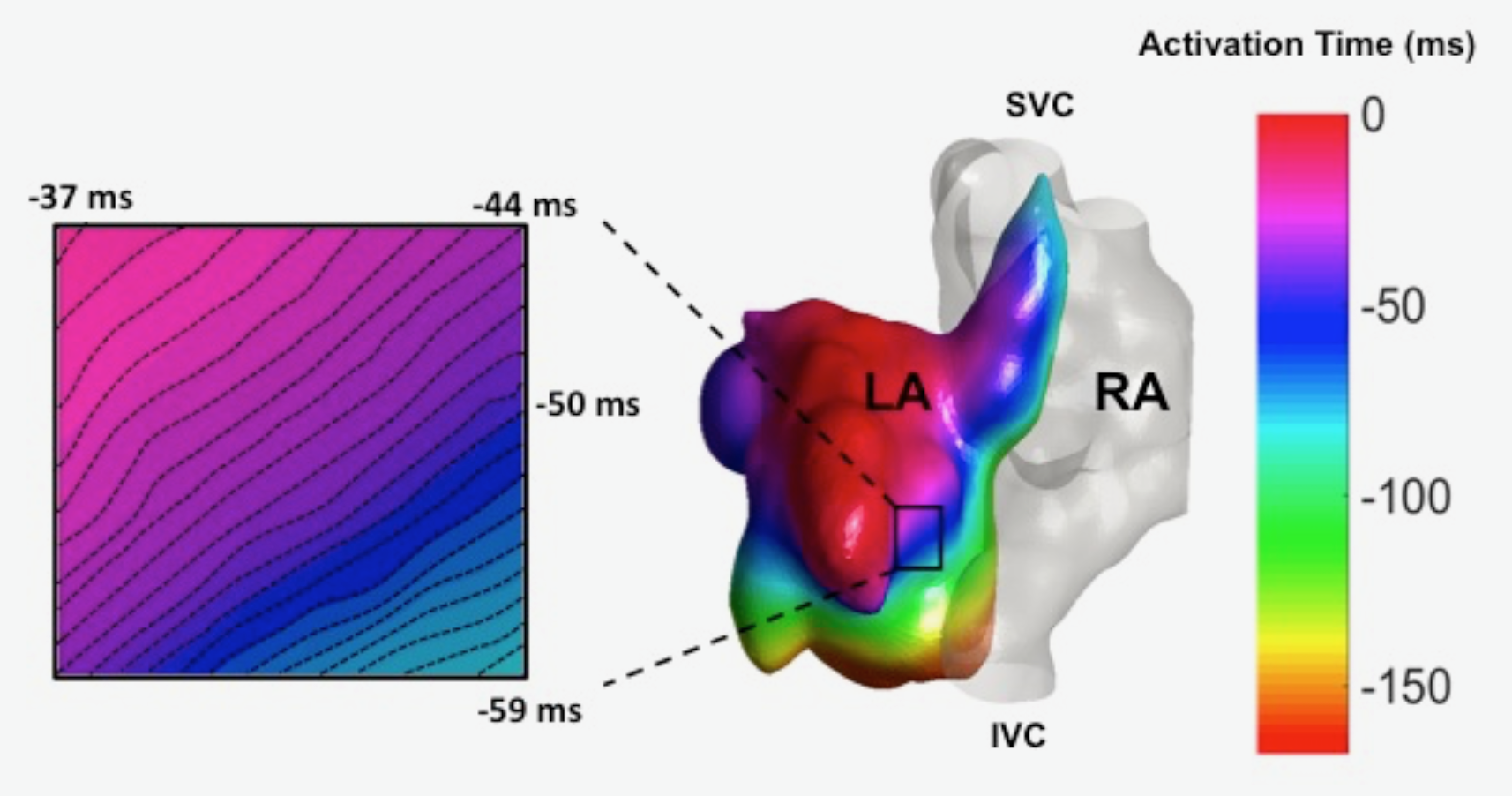 The Ranjan Laboratory, headed by Ravi Ranjan, MD, PhD, focuses on developing a better understanding of arrhythmia mechanisms and optimizing the ablation procedure. The lab is using a combination of high density electrical mapping and imaging in an animal model combined with computational modeling to develop a better understanding of arrhythmia mechanisms. To optimize the ablation procedure, the team uses MRI to quantify tissue changes including reversible edema over time for different energy sources and ablation parameters to develop the optimal ablation technique. Link to lab summary page on CVRTI
The Ranjan Laboratory, headed by Ravi Ranjan, MD, PhD, focuses on developing a better understanding of arrhythmia mechanisms and optimizing the ablation procedure. The lab is using a combination of high density electrical mapping and imaging in an animal model combined with computational modeling to develop a better understanding of arrhythmia mechanisms. To optimize the ablation procedure, the team uses MRI to quantify tissue changes including reversible edema over time for different energy sources and ablation parameters to develop the optimal ablation technique. Link to lab summary page on CVRTI 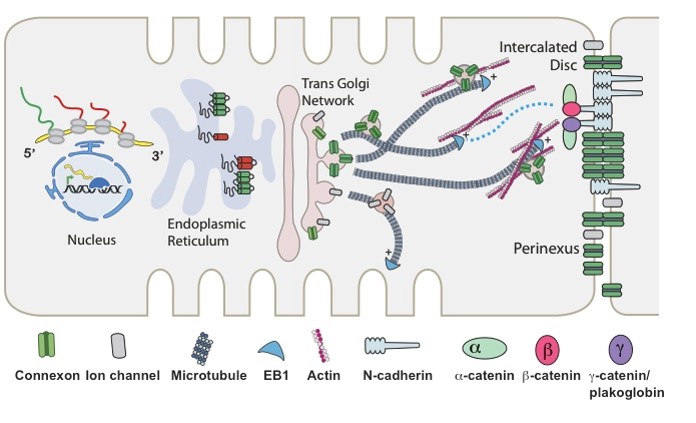 The Shaw Laboratory, headed by Robin Shaw, MD, PhD, study how cardiac ion channels are formed and how channels are targeted to specific subdomains of cardiac cell membrane in both healthy and failing heart muscle. Link to lab summary page on CVRTI
The Shaw Laboratory, headed by Robin Shaw, MD, PhD, study how cardiac ion channels are formed and how channels are targeted to specific subdomains of cardiac cell membrane in both healthy and failing heart muscle. Link to lab summary page on CVRTI 
