
The Shaw Laboratory
The Shaw Laboratory is located within the Nora Eccles Harrison Cardiovascular Research and Training Institute (CVRTI) and is focused on understanding the cell biology of heart arrhythmias and heart failure progression. Members of the lab study how cardiac ion channels are formed and how channels are targeted to specific subdomains of cardiac cell membrane in both healthy and failing heart muscle. Shaw Lab researchers combine a broad spectrum of backgrounds from talented basic scientists to medical students and clinical cardiologists. The lab research includes the mechanisms of RNA translation, cytoskeleton-based delivery of channels, the mechanisms of heart failure progression, and clinical studies of patients with heart failure. This “cell to bedside” approach is designed to develop novel diagnostics and therapeutics for failing hearts.
Visit Shawlab
Featured Publications
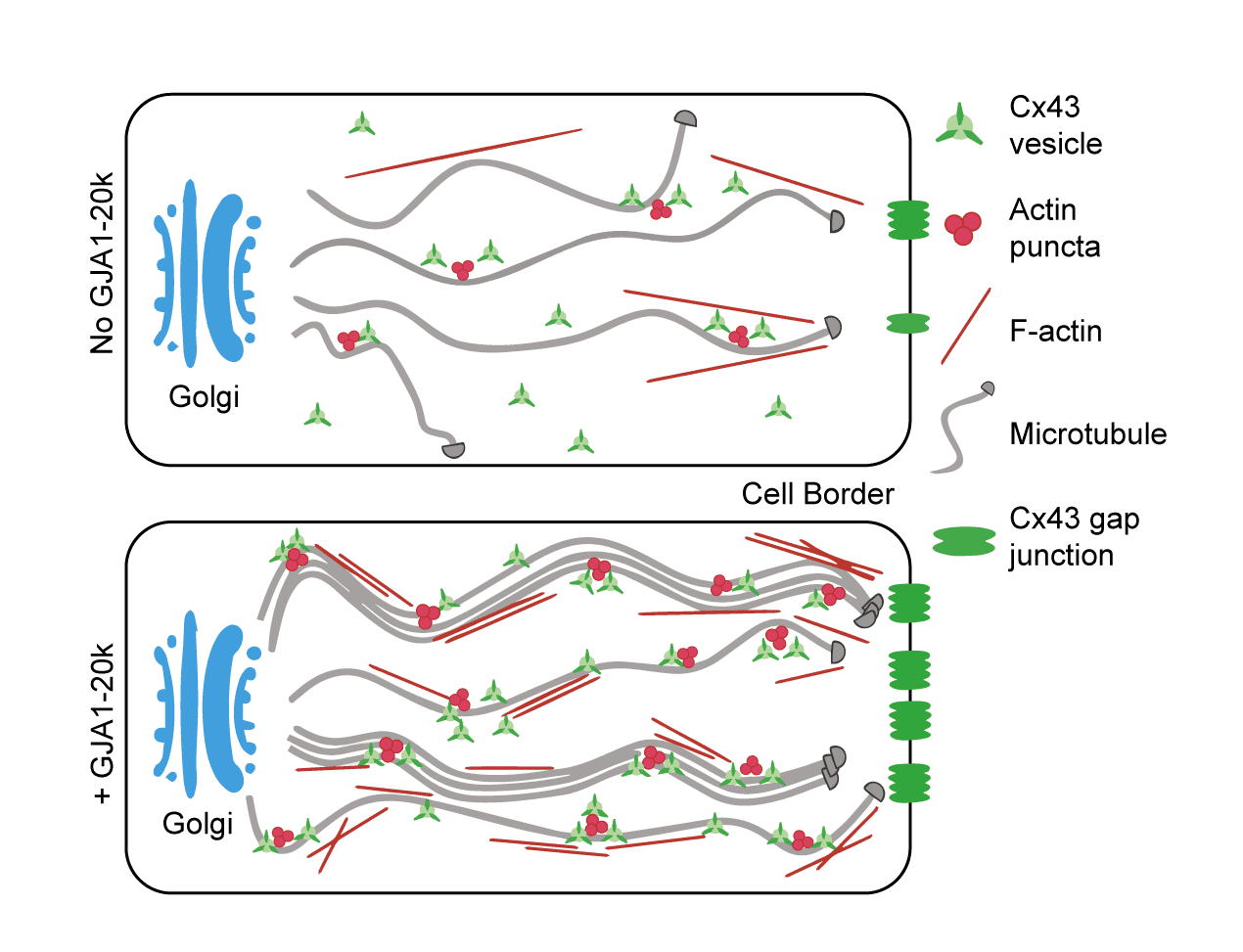 | A truncated isoform of Connexin43 caps actin to organize forward delivery of full-length Connexin43https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/39737876/ | This study asks how the Connexin43 (Cx43) gap junction channel knows how to arrive at its correct plasma membrane subdomain. The authors find that GJA1-20k, an internally translated peptide isoform of Cx43, surprisingly functions as an actin capping protein, physically arranging actin as a pathway to be followed by microtubules and, in turn, enabling microtubule-based delivery of full-length Cx43 hemichannels to Cx43 relevant membrane domains. | Baum, Rachel; Nguyen, Vu D; Maalouf, Mario; Shimura, Daisuke; Waghalter, Miriam; Srapyan, Sargis; Jin, Qianru; Kuzmanovich, Lucas; Gaffney, Adelaide T; Bell, Bridger R; Xiao, Shaohua; Palatinus, Joseph A; Kléber, André G; Grintsevich, Elena E; Hong, TingTing; Shaw, Robin M. A truncated isoform of Connexin43 caps actin to organize forward delivery of full-length Connexin43.J Cell Biol, vol. 224, no. 3, 2025, ISSN: 1540-8140. |
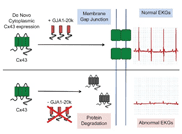 | Auxiliary Trafficking Subunit GJA1-20k Protects Connexin43 fromf Limits Ventricular Arrhythmias. https://www.jci.org/articles/view/134682 | This study introduces how a protein formed by internal translation of Connexin43 mRNA is essential for the electrical communication of each heartbeat. Without it, arrhythmias and sudden death occur. In a broader sense, the study explains how previously unknown proteins are generated and required for heart function, expanding our body’s repertoire of protein diversity | Xiao S, Shimura D, Baum R, Hernandez DM, Agvanian S, Nagaoka Y, Katsumata M, Lampe PD, Kleber AG, Hong T, Shaw RM. Auxiliary Trafficking Subunit GJA1-20k Protects Connexin43 from Degradation and Limits Ventricular Arrhythmias. JCI, 2020; 130(9):4858-4870. |
 | Cardiac BIN1 Folds T-tubule Membrane, Controlling Ion Flux and Limiting Arrhythmia. https://www.nature.com/articles/nm.3543 | This study introduces a new concept of how heart muscle is organized and identifies a new cardiac protein (cardiac BIN1 or da d d dcBIN1), which is responsible for the microarchitecture of heart muscle cells. cBIN1 is important as both a diagnostic for patients with heart failure, and therapeutic for patients with either heart failure with reduced ejection fraction (HFrEF) or heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). | Hong T, Yang H, Zhang S, Cho HC, Kalashnikova M, Sun B, Zhang H, Bhargava A, Grabe M, Olgin J, Gorelik J, Marbán E, Jan LY, Shaw RM. Cardiac BIN1 folds T-tubule membrane, controlling ion flux and limiting arrhythmia. Nature Medicine, 2014; 20:624-32. |
The Shaw Lab Research Team

Robin Shaw, MD, PhD
Principal Investigator

Daisuke Shimura, PhD
Research Assistant Professor

Tara Hitzeman, MPH
Biostatistician

Jen Hunter
Lab Specialist/Lab Manager

Pia Balmaceda, MD
Postdoctoral Research Associate

Vu Nguyen
Graduate Research Assistant (RA)

Mario Maalouf, MD
Postdoctoral Research Associate u6049542@utah.edu

