Aneurysm Treatments: From Monitoring to Surgical Interventions
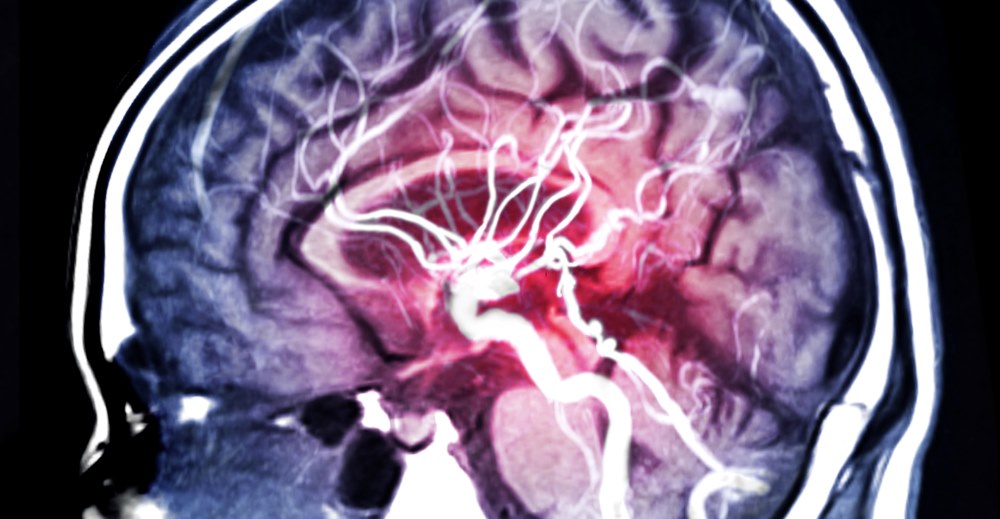
An aneurysm is an abnormal bulge in the wall of a blood vessel. It can occur in many parts of the body, including the brain. Cerebral aneurysms, also called brain aneurysms, are very dangerous since they are likely to rupture and cause life-threatening hemorrhages. To manage this significant condition, awareness of the treatment options, recovery process, and potential for early detection is essential.
Brain Aneurysm Treatment Without Surgery
Not every brain aneurysm necessitates surgery. Sometimes, aneurysms are small and don’t cause symptoms. Doctors may choose to watch and wait while incorporating CT or MRI scans to monitor the shape and size of the aneurysm over time. The main goal is to be sure it doesn’t change or grow in a way that might increase the chance of a rupture.
Patients are often asked to make lifestyle changes to lessen the chances of growth or rupture in the future. This might include avoiding smoking, controlling blood pressure, managing stress, and reducing alcohol consumption. Medications can also be provided to help with blood pressure and prevent strain on the blood vessels.
Brain Aneurysm Treatment and Recovery
If an aneurysm might soon rupture (or already has), other types of treatment are required. However, the chosen treatment depends on the aneurysm’s shape, location, and size. The determining factor may also be how healthy the patient is.
Non-Invasive Treatment: Endovascular Coiling
One of the most common procedures is endovascular coiling. This is minimally invasive and includes inserting a catheter into the bloodstream. It often goes in through the groin and is then guided to the aneurysm site. Small coils are then put into the aneurysm to promote blood clotting and seal it off from the artery.
Recovery Time from Endovascular Coiling Recovery from this procedure is quicker than general surgery, and many patients are back to regular activities in a few weeks.
Invasive Treatment Option: Surgical Clipping
Surgical clipping is another but more serious treatment option. A neurosurgeon will put a metal clip at the base of the aneurysm to stop the blood flow coming into it. While this is a highly effective method, the skull needs to be opened, so the recovery period can be quite lengthy. Depending on their health and the surgery’s complexity, most people need weeks to months to recover fully.
Brain Aneurysm Medical Procedure
A new technique is being used for some kinds of aneurysms, especially those with a challenging shape or a large size. Flow diversion is frequently used in these situations. The basic idea is that a stent-like flow diverter sits around the aneurysm’s neck. The device moves blood away from the aneurysm so the blood vessel wall can start to heal.
Recovering and Post-Treatment Care
No matter what type of treatment was done for a brain aneurysm, the recovery necessitates careful follow-up and rehabilitation. Patients often need to do regular imaging tests to make sure the aneurysm has been adequately treated. This is also done to watch for any signs of a recurrence. Rehabilitation efforts may include things like occupational therapy, physical therapy, and speech therapy to handle any neurological issues caused by the aneurysm or its treatment.
Can You Detect an Aneurysm Before It Happens?
One of the questions that people ask more than anything is whether aneurysms can be detected before causing symptoms or rupturing. Most of the general population should not worry about routine screening for aneurysms, but it can be a good idea to incorporate early detection strategies for high-risk people.
For instance, those with a family history of aneurysms or those with certain genetic disorders (such as connective tissue disorders or polycystic kidney disease) and people with a history of aneurysms are at high risk. In these cases, a doctor may recommend MRI or CT angiography to detect aneurysms early.
Final Thoughts
Aneurysms of all types, especially those in the brain, are a considerable health risk. However, several treatment options are available to manage and reduce these risks. The treatment is designed for the patient’s specific needs, from simple monitoring to advanced surgical interventions like flow diversion, surgical clipping, and endovascular coiling.
Detecting aneurysms early is an essential part of managing them. For high-risk people, regular screening and understanding the symptoms can help with diagnosis and treatment to save lives. While medical technology advances, the future may hold even better options for treating and detecting aneurysms, which could improve patient outcomes around the globe.


